Exploring the Difference between Electric and Electronic Circuits
Introduction
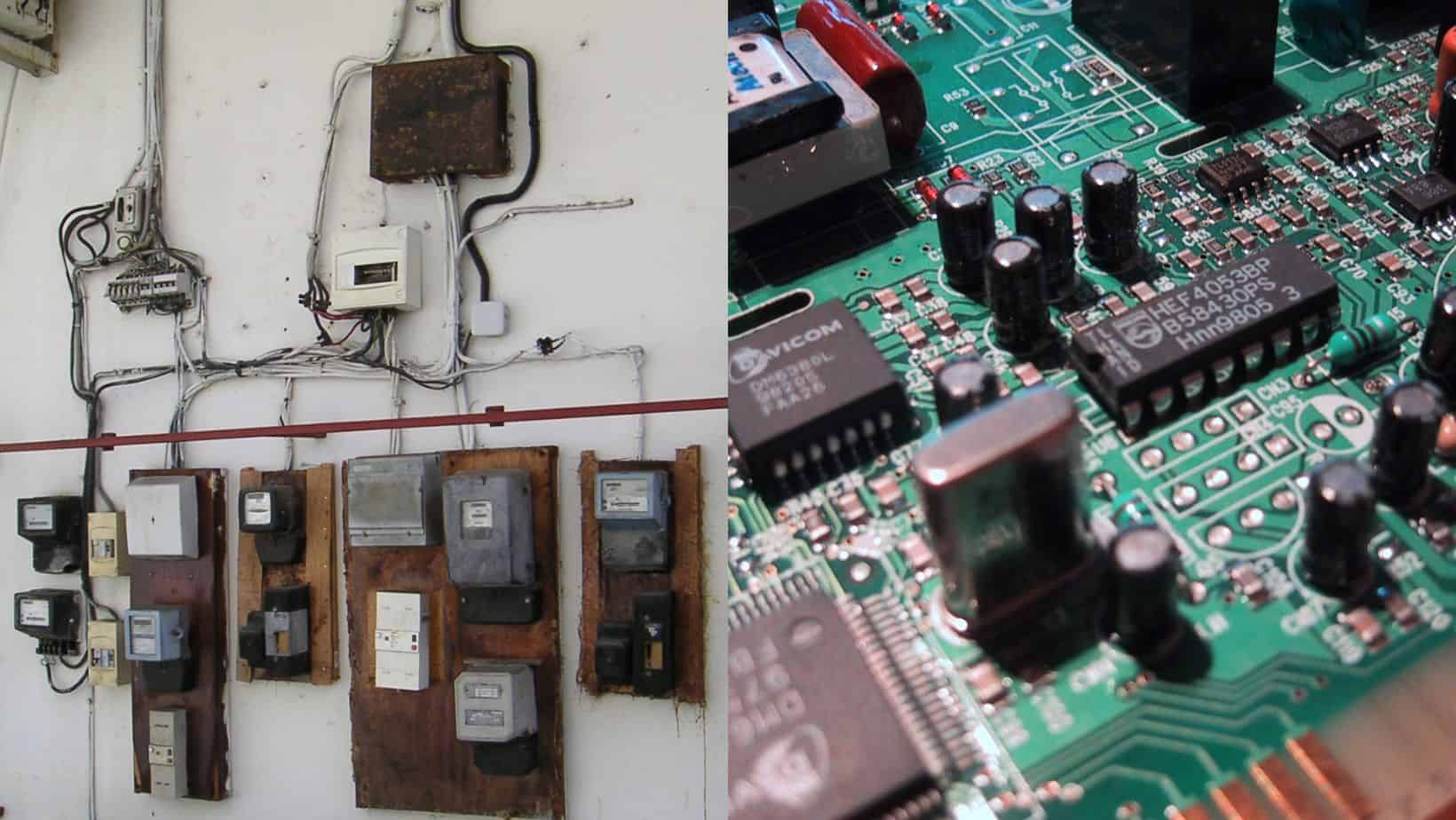
Electric and electronic circuits are two fundamental types of circuits that power our world. While electric circuits are responsible for large-scale power distribution and simpler applications, electronic circuits power more advanced digital technologies through miniaturized, low-power designs. Understanding the difference between these two types of circuits is crucial for fields like engineering and consumer technology.
Electric Circuit
An electric circuit is a closed loop that allows electric current to flow continuously. It consists of a power source (such as a battery or generator), conductive pathways (wires), and a load (a device that uses electric energy). Common examples of loads are light bulbs, motors, and heating elements.
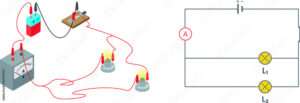
- Power source: The power source provides the energy that drives the circuit. Common power sources include batteries, generators, and solar cells.
- Conductive pathways: Conductive pathways allow the electric current to flow through the circuit. Common conductive materials include copper and aluminium.
- Load: The load is the device that uses the electric energy from the circuit. Common loads include light bulbs, motors, and heating elements.
Functionality of Electric Circuits
Electric circuits are designed to deliver relatively high power over distances using thicker conductors and higher line voltages like 110/220V. They are used for simple tasks like controlling basic functions like lighting, and operating appliances and machinery.
Electronic Circuit
An electronic circuit is a type of circuit that uses active electronic components like transistors, diodes, resistors, and capacitors to process signals and perform logical functions. These components precisely control the flow of small electric currents to enable complex tasks like amplification, oscillation, and data processing.
- Active components: Active components amplify or modulate signals in electronic circuits. Common active components include transistors, diodes, and op-amps.
- Passive components: Passive components store energy, establish voltage divisions, or filter signals in electronic circuits. Common passive components include resistors, capacitors, and inductors.
Functionality of Electronic Circuits
Electronic circuits are designed to handle low-power signals using miniaturized components. They are capable of advanced functions like data processing, signal modulation, and other operations by precisely controlling small electric currents.
Key Differences between Electric and Electronic Circuits
| Characteristic | Electric Circuits | Electronic Circuits |
|---|---|---|
| Power handling | High | Low |
| Complexity | Less complex | More complex |
| Applications | Large-scale power distribution and simpler applications | More advanced digital technologies |
| Examples | Household wiring, streetlights, power grids, electric motors, heating elements | Computers, smartphones, televisions, radios, medical devices |
Applications of Electric and Electronic Circuits
- Electric circuits are used in a wide range of applications, including:
- Power generation and distribution
- Lighting
- Heating and cooling
- Industrial automation
- Transportation
- Electronic circuits are used in even more diverse applications, including:
- Computing
- Telecommunications
- Consumer electronics
- Medical devices
- Aerospace and defense
Electric and Electronic Circuits Complexity
Aside from the basic components and functionality described above, electric and electronic circuits can also incorporate more complex elements such as microcontrollers, integrated circuits, and sensors. These elements allow for the development of highly sophisticated circuits that can perform complex tasks such as data processing, signal control, and automation.
Electric and Electronic Circuits in the Future
Electric and electronic circuits are constantly evolving, with new technologies and applications emerging all the time. The development of smart grids and electric vehicles is already increasing the demand for more efficient and intelligent power distribution systems. In addition, the rise of artificial intelligence and the Internet of Things (IoT) is creating new opportunities for electronic circuits to be used in a variety of innovative applications.
How Electric and Electronic Circuits Are Used In Cutting-Edge Technologies
- Smart grids: Smart grids are emerging as a new way to manage and distribute electric power. They use a variety of sensors and electronic devices to monitor and control the grid in real-time, which can help to improve efficiency and reliability.
- Electric vehicles: Electric vehicles are becoming increasingly popular as a way to reduce emissions and improve fuel efficiency. They rely on a variety of electric and electronic circuits, including batteries, motors, and power electronics.
- Wearable devices: Wearable devices like smartwatches and fitness trackers are becoming more and more popular. They use a variety of electronic sensors and circuits to track the user’s activity and health.
The future of electric and electronic circuits is very bright. As new technologies and applications emerge, we can expect to see even more innovative and powerful circuits developed.
Conclusion
Electric and electronic circuits play vital roles in our world, powering everything from our homes and businesses to our cars and smartphones. By understanding the difference between these two types of circuits, we can better appreciate the complex technologies that rely on them.
FAQs about Electric and Electronic Circuits
What is an electric circuit?
An electric circuit is a closed loop that allows electric current to flow continuously. It consists of three essential components:
- A power source, such as a battery or generator, provides the driving force for the current.
- Conductive pathways, such as wires, allow the current to flow.
- A load, such as a light bulb or motor, consumes electrical energy.
What is an electronic circuit?
An electronic circuit is a type of electric circuit that uses active electronic components, such as transistors and diodes, to process signals and perform logic functions. These components can amplify, amplify, and modulate signals, as well as perform complex mathematical operations.
What is the main difference between electric and electronic circuits?
The key difference between electric and electronic circuits is their primary function. Electric circuits are primarily used for power distribution and control, while electronic circuits are primarily used for signal processing and computation. Electric circuits typically operate at higher voltages and currents than electronic circuits.
What voltage and current levels do electric and electronic circuits operate at?
Electric circuits typically operate at line voltages of 110/220V AC, while electronic circuits typically operate at lower DC voltages below 30V. Electric circuits are also designed to handle higher currents than electronic circuits.
How are electric and electronic circuits controlled?
Electric circuits are typically controlled using manual switches, while electronic circuits are typically controlled using programmable logic gates and microcontrollers. This allows electronic circuits to perform complex tasks, such as data processing and automation.
What size are the components in electric and electronic circuits?
Components in electric circuits are typically larger than components in electronic circuits. This is because electric circuits need to dissipate more heat from higher power loads. Electronic components are highly miniaturized using semiconductor manufacturing, which allows them to be packed into small devices such as smartphones and computers.
What are some applications of electric and electronic circuits?
Electric circuits are used in a wide variety of applications, including power generation and distribution, industrial automation, transportation, construction, and home appliances. Electronic circuits are used in consumer electronics, medical devices, telecommunications, aerospace and defence, and industrial automation.
Are electric and electronic circuits always separate?
No, electric and electronic circuits are often combined in the same device. For example, a smartphone contains both electric circuits to power the display and other components, as well as electronic circuits to process data and perform other functions.
Which type of circuit handles higher current?
Electric circuits are designed to handle higher currents than electronic circuits. This is because electric circuits are typically used to power devices that require more power, such as motors and appliances.
Can electronic circuits use AC?
Yes, some electronic circuits can use AC power. However, most electronic circuits operate on regulated DC power. Switch mode power supplies are used to convert AC power to DC power for electronic circuits.
Do electric and electronic circuits contain the same components?
Both electric and electronic circuits use passive components, such as resistors, capacitors, and inductors. However, electronic circuits also use active components, such as transistors and diodes.
Can an electric circuit perform logic?
Simple electric relay circuits can mimic logic to an extent, but electronic components are necessary for robust digital computations.
Which type of circuit evolved earlier?
Electric circuits for fundamental power distribution predate the widespread use of transistors and integrated circuits in electronic technology by over a century.
Are higher voltages always electric?
No, some specialized electronic equipment, such as switchgear and radar transmitters, require higher voltages. However, these voltages are typically controlled through electronic switching rather than simple conduction.
Is one type of circuit preferable over the other?
Both electric and electronic circuits play indispensable but distinct roles. Electric circuits maximize efficiency at scale, while electronics add programmability for advanced automation and computation.